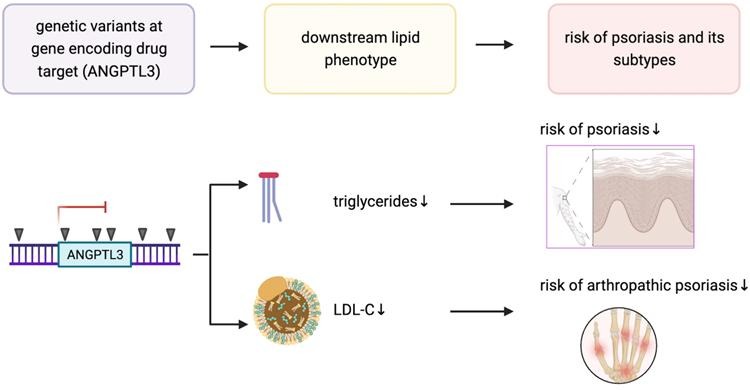
Genetically mimicked effects of evinacumab on psoriasis: a drug target Mendelian randomization study
▪ Author : Z Yang, W Xiao, Z Zhuang, S Zhan, M Wang, Y Wu, T Huang, R Li
▪ Keyword : psoriasis, angiopoietin-like 3, evinacumab, lipid metabolism, Mendelian randomization
▪ Content : Background and Objectives: Dyslipidemia has been reported to contribute to the psoriasis pathogenesis. Thus, evinacumab, a novel lipid-lowering drug targeting angiopoietin-like 3, may have therapeutic potential to treat and/or manage psoriasis. Methods and Study Design: Summary statistics were obtained from genome-wide association studies addressing psoriasis (FinnGen Consortium; n=216,752) and serum lipid concentrations (United Kingdom Biobank; n=403,943–440,546). Two-sample Mendelian randomization analyses were conducted to evaluate the associations of serum lipid concentrations and genetically mimicked effects of evinacumab, respectively, with the risks of psoriasis and its subtypes.