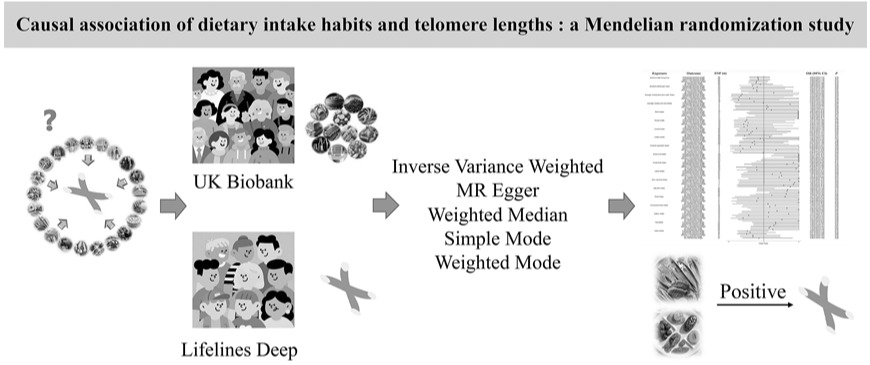
Causal association of dietary intake habits and telomere lengths: A Mendelian randomization study
▪ Author : J Chen, Z Liu, Y Nan, H Liu, Z Ren, J Liu, D Liu, R Qi
▪ Keyword : dietary factors, telomere length, Mendelian randomization, causal relationship, healthy diet reference
▪ Content : Background and Objectives: Healthy diets are crucial in disease prevention and balanced diets can slow telomere shortening. Currently, it is still unclear which dietary factors are causally related to telomere length. Methods and Study Design: The inverse variance weighted, Mendelian Randomization-Egger, weighted median, simple mode, and weighted mode methods were used. Additionally, heterogeneity, pleiotropy, MR-PRESSO and leave-one-out tests were conducted to ensure accuracy. Outcomes included granulocyte, lymphocyte, naive T-cell, memory T-cell, B-cell, and natural killer-cell telomere lengths. Exposures included alcohol intake frequency, alcoholic drinks per week, average weekly beer plus cider intake, average weekly red wine intake, intake of beef, bread, cereal, coffee, cooked v...