Micronutrient status of patients with diabetic foot: A systematic review
▪ Author : S Batarbekova, D Zhunussova, G Derbissalina, Z Bekbergenova, N Maksimova, A Umbetzhanova, E Kelimber
▪ Keyword : diabetes mellitus type 2, diabetic foot ulcers, micronutrient status, vitamins, micronutrients
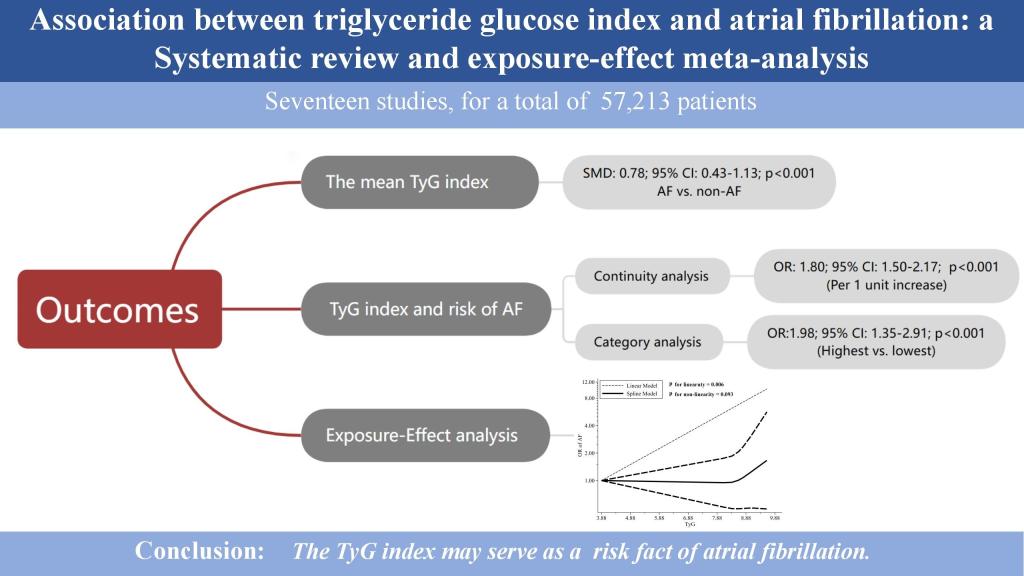
▪ Content : Background and Objectives: Micronutrient status encompasses a range of indicators that reflect the levels and balance of macro- and microelements, as well as vitamins within the body. These essential substances, required in minimal amounts, are crucial for supporting normal physiological processes, immune system functioning, and tissue repair. The aim of this systematic review is to summarize data on the deficiency or excess of microelements, macroelements, and vitamins in patients with diabetic foot ulcers. Methods and Study Design: Databases were searched for studies on vitamin, macronutrient, micronutrient levels and their impact on the course, treatment and healing of diabetic foot ulcers.