Abstract
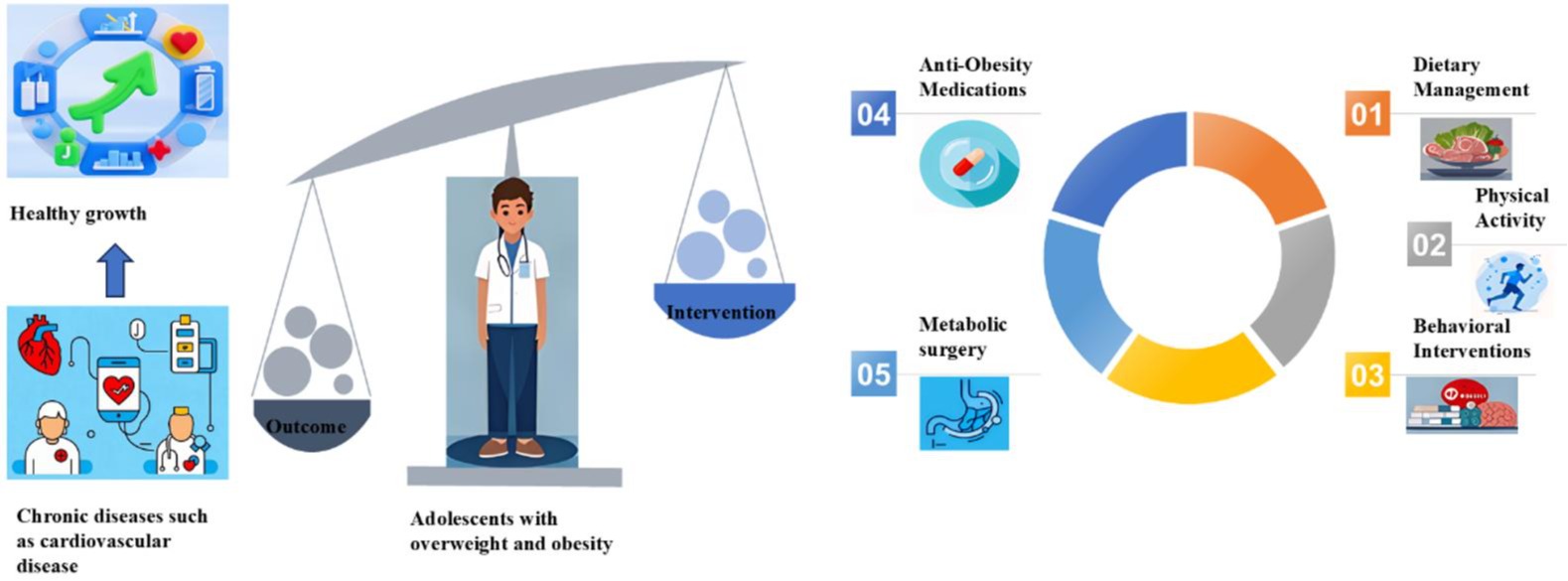
Background and Objectives: The prevalence of overweight or obesity in adolescents is steadily increasing in most countries around the world. Adolescent obesity increases the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, and is associated with negative health consequences, increasing the burden on health services. Methods and Study Design: Literature searching was conducted in PubMed and Google Scholar using the keywords “overweight”, “obesity”, “adolescent”, “weight management”, “dietary management” and “nutritional intervention” combined with Boolean operators “AND” and “OR”. Results: Multicomponent lifestyle interventions, including diet, physical activity, and behavioural interventions, are used as first-line treatment for anti-obesity interventions. Dietary management methods such as energy-restricted diet are beneficial to control body weight, and it is important to ensure their normal growth and development while restricting energy. Conclusions: Multicomponent lifestyle intervention is the first choice for anti-obesity intervention. It is recommended that intensive health behaviour lifestyle treatment combined with anti-obesity medications be used at the beginning of anti-obesity treatment in adolescents.
Download this article
 PDF format
PDF format