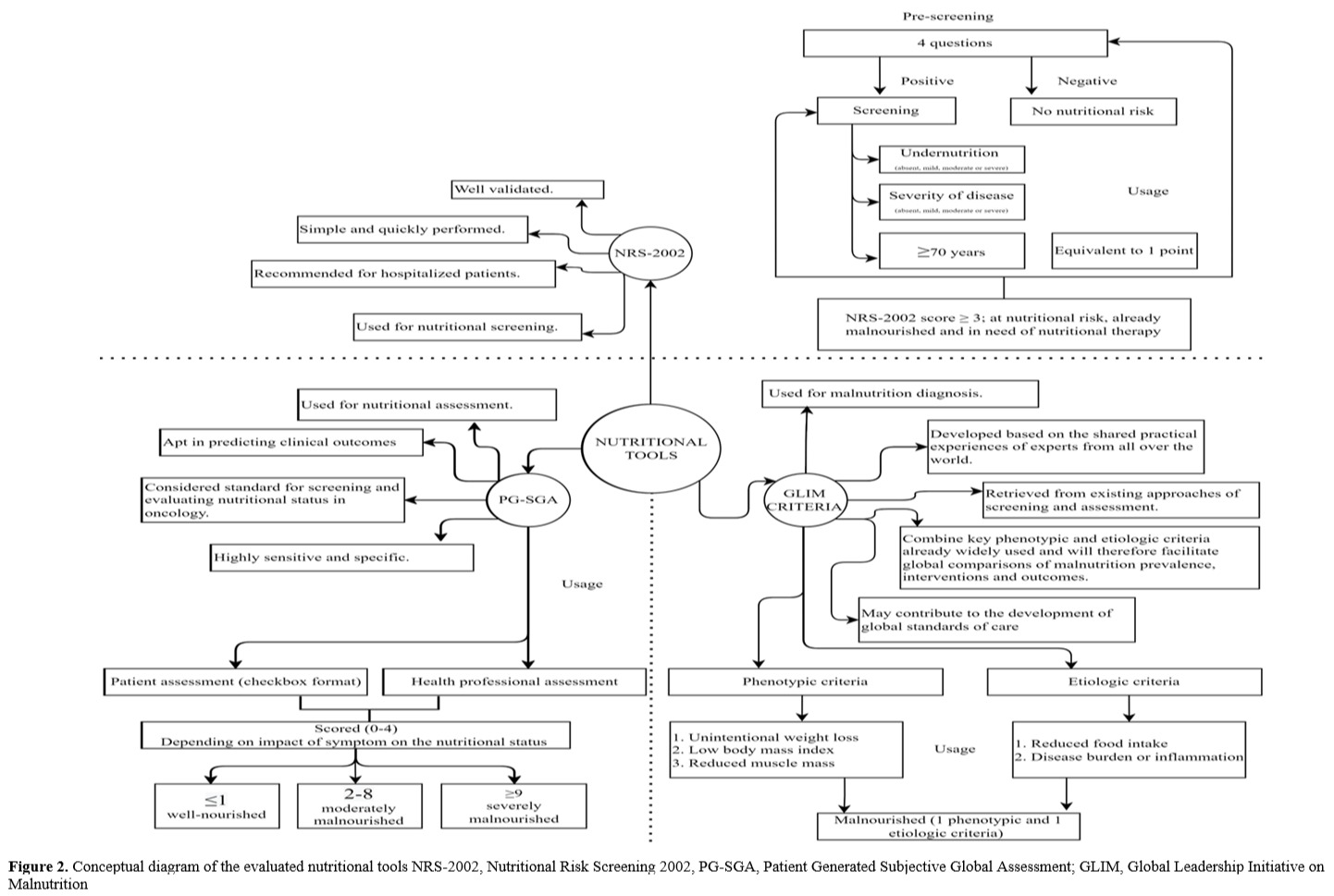
Efficacy and safety of parenteral nutrition with iron sucrose for anemia prevention in preterm infants: A randomized, double-blind controlled study
▪ Author : Q Wu, Y Wang, W Wang, Y Zhang, W Yan, L Lu, Y Tao, Q Tang
▪ Keyword : preterm infants, anemia, iron sucrose, parenteral nutrition
▪ Content : Background and Objectives: Our objective is to study the efficacy and safety of parenteral nutrition (PN) with iron sucrose to prevent anemia in preterm infants. Methods and Study Design: We performed a ran-domized, double-blind controlled trial in which preterm infants were divided into five groups randomly: a control group (PN without iron sucrose, namely group Iron-0), and intervention groups (PN with iron sucrose 100 μg/kg/d, 200 μg/kg/d, 300 μg/kg/d and 400 μg/kg/d, namely group Iron-1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively). The indicators were red blood cell (RBC) parameters, iron storage and oxidant stress.