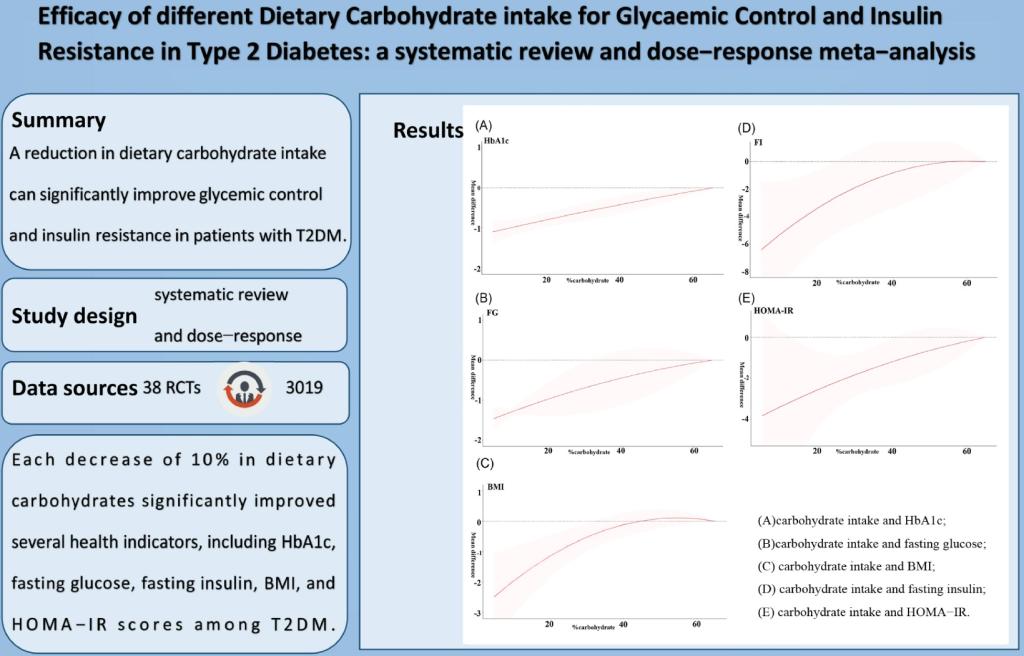
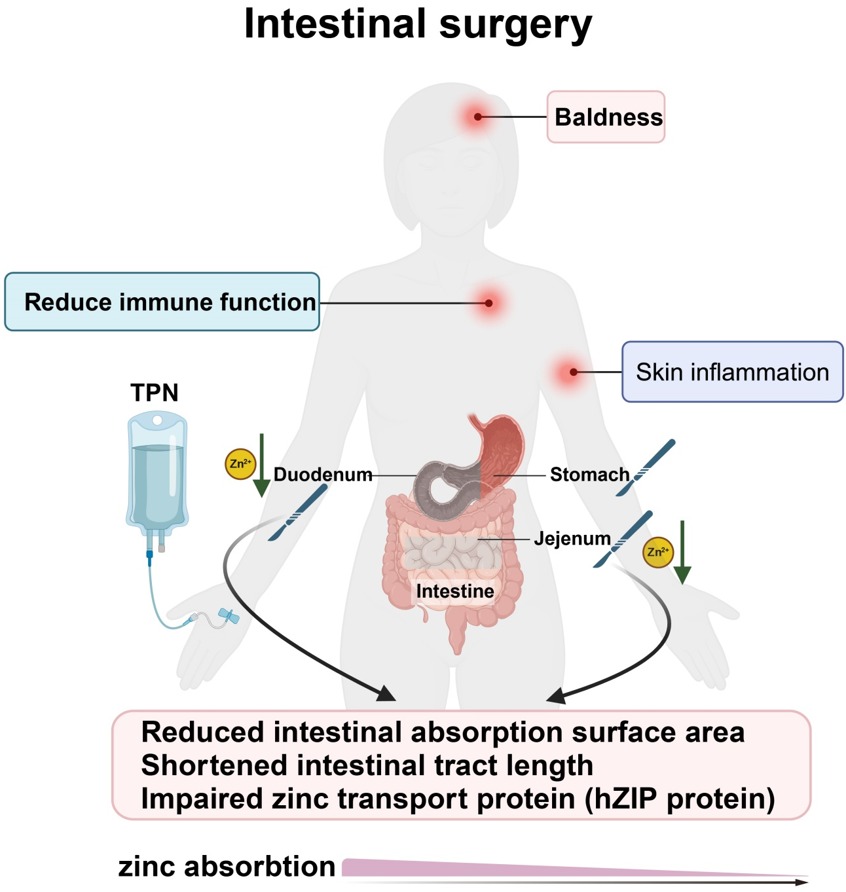
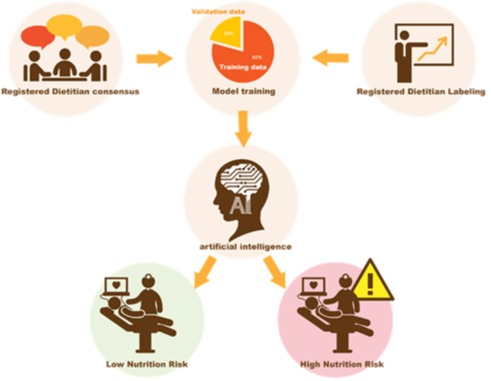
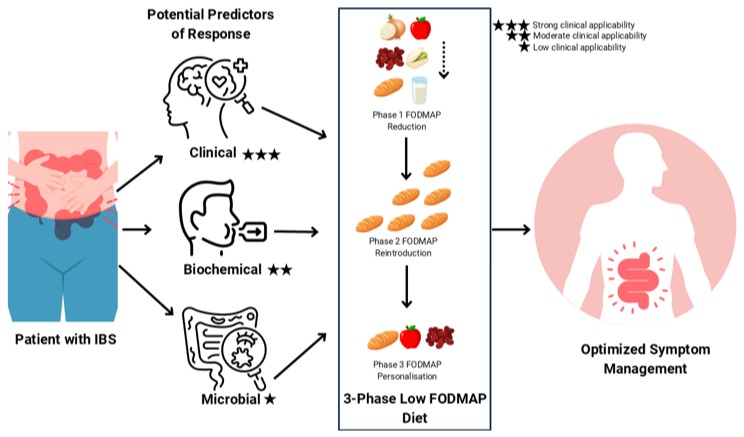
Exploring management of acrodermatitis
▪ Author : H Tang, Y Yang, F Yao, Q Xiong, M Yin, Y Liao, L Li, F Hu and K Li
▪ Keyword : acrodermatitis enteropathica, acquired zinc deficiency, zinc gluconate, skin biopsy, total parenteral nutrition
▪ Content : Background and Objectives: Acquired acrodermatitis enteropathica (AE), a rare dermatological condition, often stems from nutritional zinc deficiency linked to prolonged total parenteral nutrition (TPN). This study aims to explore the pathogenesis, clinical characteristics, and treatment approaches for AE, emphasizing the importance of early recognition and intervention. Methods and Study Design: A 51-year-old female patient with acquired AE presented with widespread erythema, pustules, and itching. A comprehensive diagnostic approach, including various tests and skin biopsy pathology, confirmed the diagnosis.