Gender-specific association of body fat mass with muscle meat-vegetable intake ratio in Shaanxi, China
▪ Author : H Jing, Y Teng, SS Chacha, Z Wang, B Zhang, J Cai, D Wang, H Yan, S Dang
▪ Keyword : muscle meat-vegetable intake ratio, body mass index, waist circumference, total body fat, visceral fat
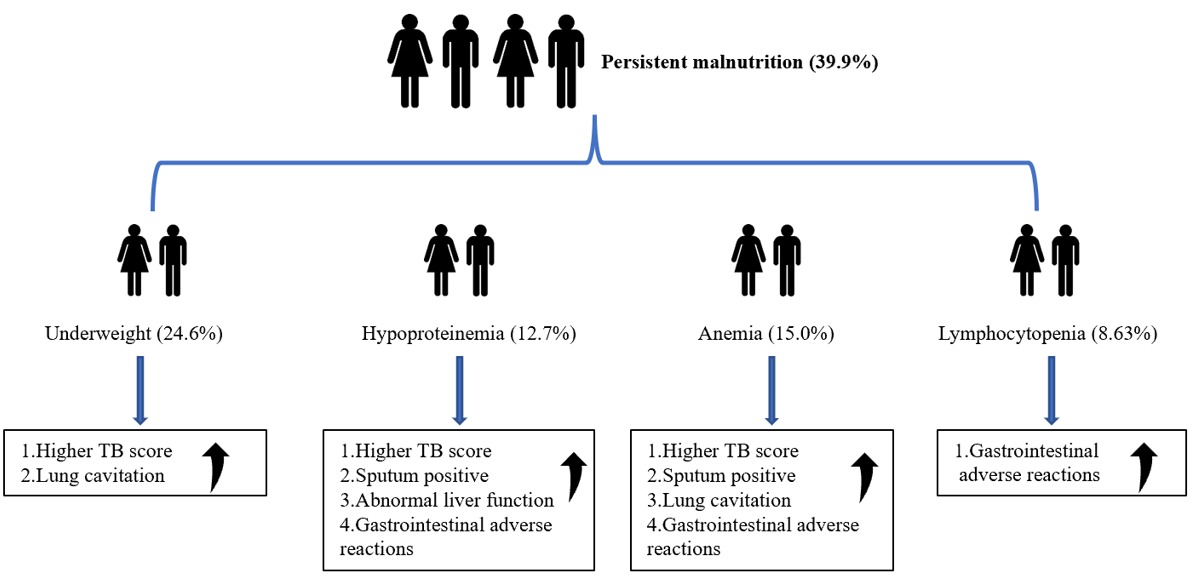
▪ Content : Background and Objectives: The effects of muscle meat and vegetable intake on body fat mass remain unclear in the general population. This study aimed to investigate the association of body fat mass and fat distribution with a muscle meat-vegetable intake (MMV) ratio. Methods and Study Design: In total, 29,271 participants aged 18–80 years were recruited from the Shaanxi cohort of the Regional Ethnic Cohort Study in Northwest China. The associations of muscle meat, vegetable and MMV ratio, as the independent variable, with body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, total body fat percentage (TBF) and visceral fat (VF), as dependent variables were evaluated by gender-specific linear regression models.