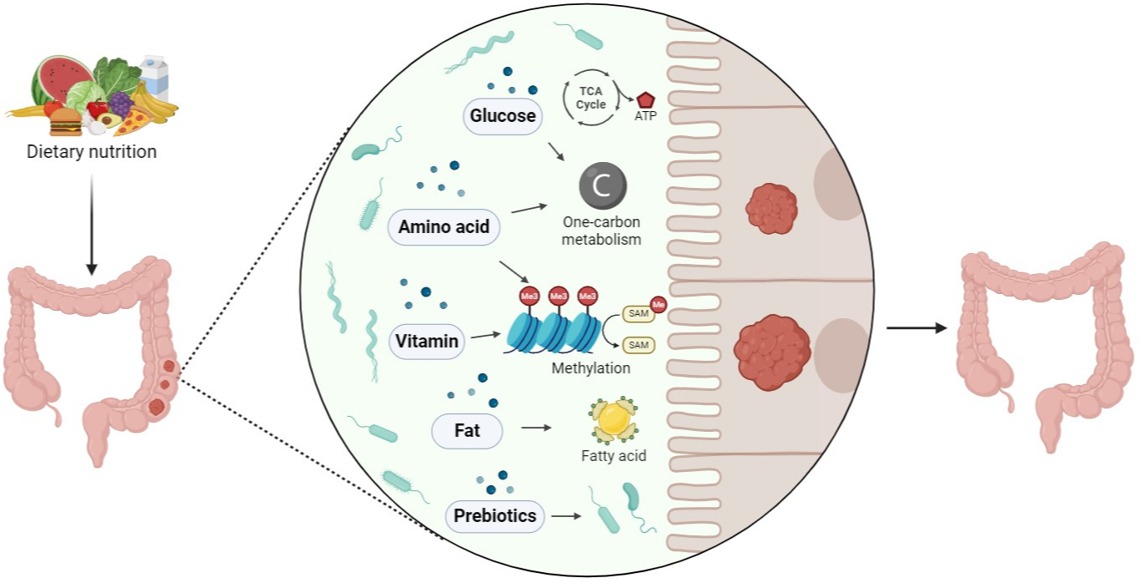
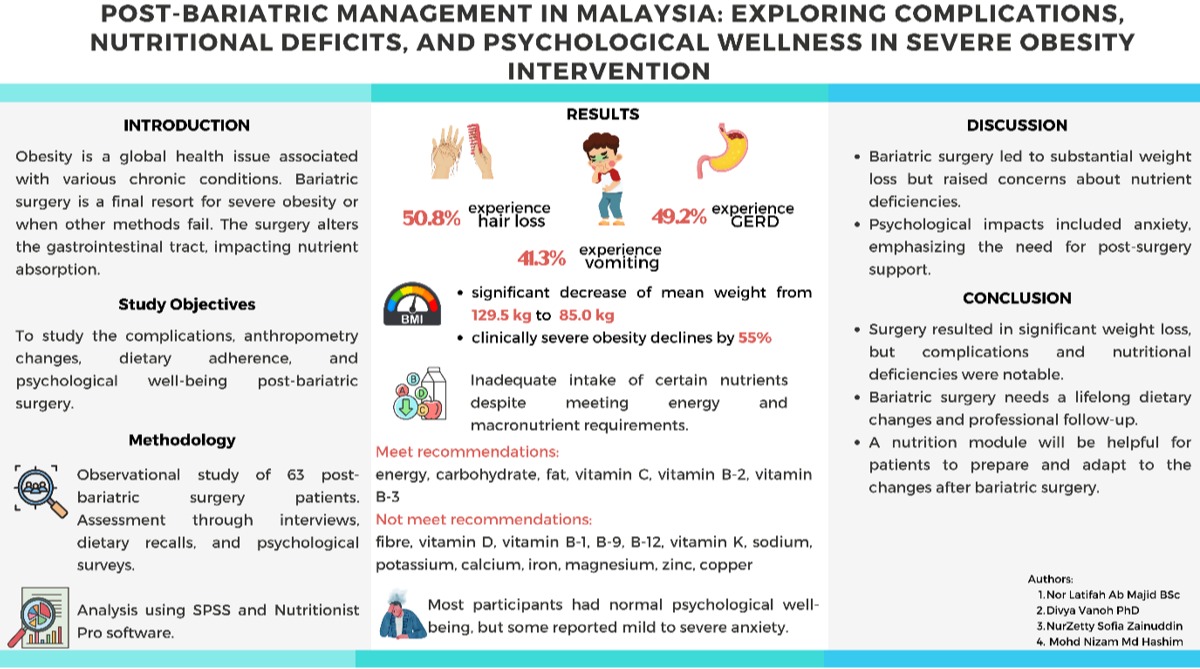
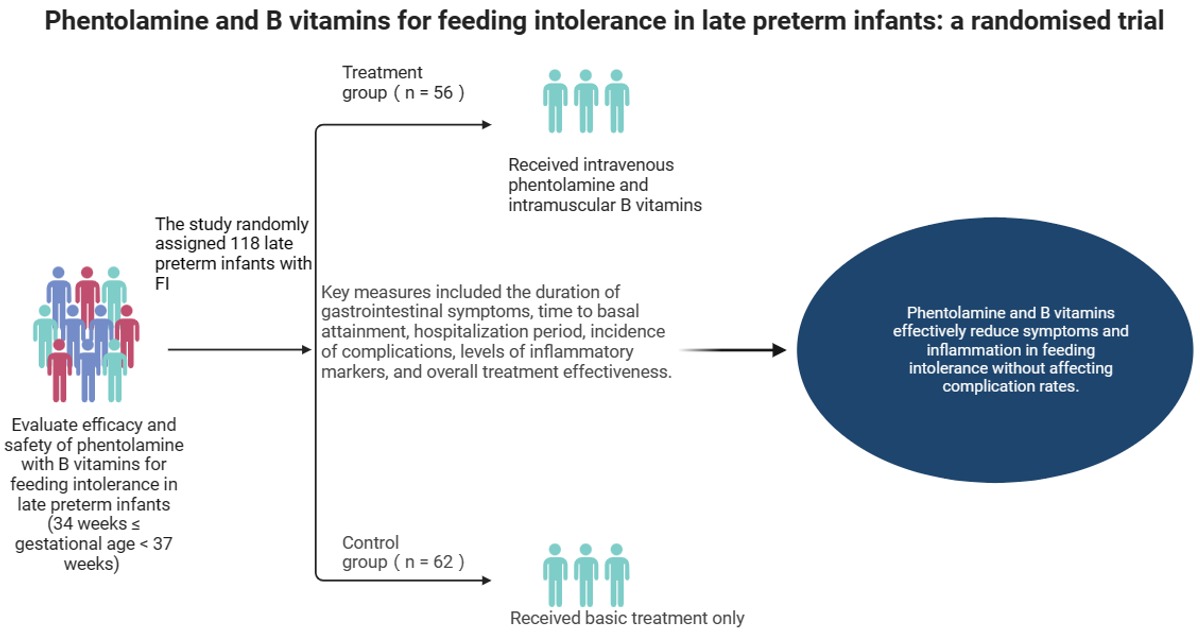
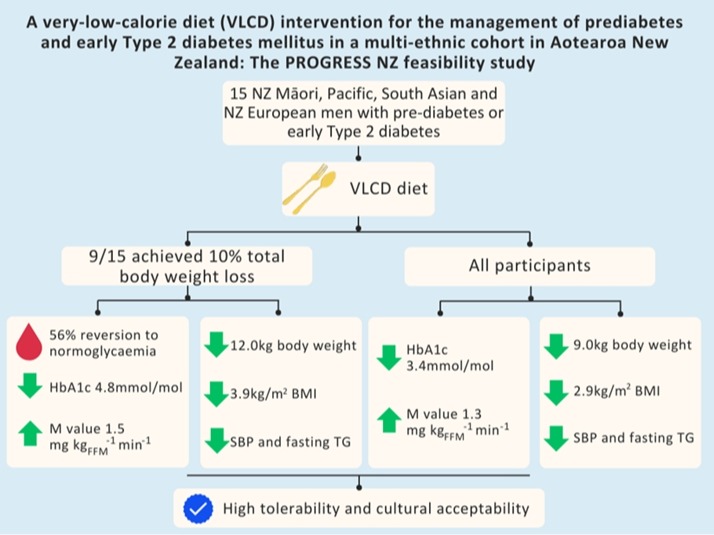
Comparative study of eating behavior between patients with mental illness and healthy controls using the Japanese version of the Dutch Eating Behavior Questionnaire
▪ Author : S Okabe, S Ito, A Goto and N Konno
▪ Keyword : DEBQ, eating behavior, obesity, mental illness, nutrition education
▪ Content : Background and Objectives: To examine the reliability and validity of the Japanese version of the Dutch Eating Behavior Questionnaire (DEBQ-J) for patients with mental illness, and to determine the characteristics of eating behavior among these patients when compared with healthy controls. Methods and Study Design: In May 2018, 120 outpatients with mental illness and 132 healthy controls were surveyed. First, exploratory factor analysis was conducted on the DEBQ-J statement responses for both patients and healthy controls. Next, reliability coefficients were calculated for the eating behavior scale scores (emotional, restrained, and external eating) extracted from the factor analysis.